Chronic stress has far-reaching effects on the human body and mind. Unlike short-term stress, which helps the body respond to immediate challenges, chronic stress occurs when the body remains in a state of heightened alertness for extended periods. Understanding these effects provides insight into how they impact various areas of life.
Physical Effects
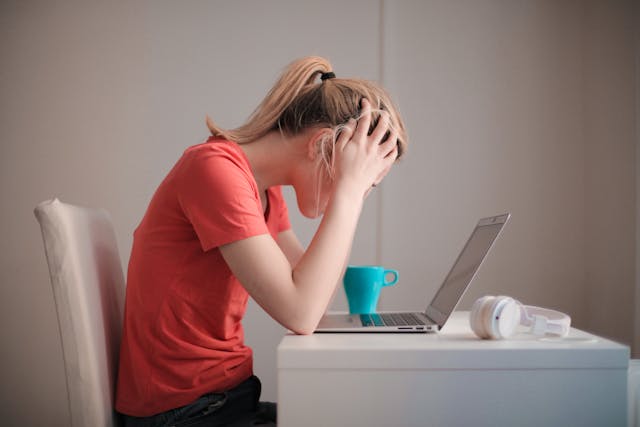
Chronic stress places a significant burden on the body’s systems. The body releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline when tension persists for a longer period. These hormones disrupt bodily functions and compromise physical health in several ways. Chronic strain can harm the cardiovascular system and elevate blood pressure levels.
Prolonged strain also affects the gastrointestinal system, possibly causing symptoms. These can include stomachaches, changes in appetite, or digestive disturbances. Inflammation can flare up due to prolonged tension and may contribute to weakened immune function. This leaves you more likely to become ill.
Sleep disruptions are another common issue linked to chronic strain. Many individuals in a prolonged state of distress struggle with insomnia or difficulty maintaining restful sleep, further taxing the body. These physical issues combined can detract from overall well-being and may require proper attention.
Mental and Emotional Impact
Chronic tension significantly interferes with mental and emotional health. Mentally, individuals experiencing prolonged strain often report difficulty with concentration, decision-making, and memory retention. Long-term stress-related hormonal imbalances may influence brain function and decrease the ability to think clearly.
Emotionally, stress amplifies negative feelings such as irritability, frustration, or sadness. This emotional strain places individuals at higher risk for conditions like anxiety or depression. Left unchecked, stress can create a cycle where emotional challenges further deepen feelings of frustration or hopelessness.
Tension even affects emotional regulation. Individuals in a perpetual stressed state may feel overwhelmed by everyday responsibilities or lack the resilience to cope with minor setbacks. This combination of mental fatigue and emotional turbulence creates challenges in daily life.
Social Implications
Chronic stress rarely remains confined to the individual—it impacts relationships and social connections as well. Stress may lead to withdrawal from friends, family, or social activities due to exhaustion or difficulty regulating emotions. This withdrawal can contribute to feelings of isolation or strain personal relationships.
Chronic strain negatively affects communication. Increased irritability or frustration may result in reactive interactions with loved ones, creating misunderstandings or conflicts. Stress can also diminish energy and patience, making it harder to engage meaningfully with others or collaborate effectively in group settings.
Professionally, ongoing tension may alter workplace relationships. Difficulties with focus or emotional regulation may reduce productivity or change how individuals are perceived by colleagues, impacting teamwork and performance. The cumulative social effects of chronic stress highlight its influence beyond personal health, emphasizing its impact on interpersonal environments.
Also Read: How to Fend Off Stress When Taking on a Long-Distance Moving Project
Managing Stress for Long-Term Health
Understanding how chronic strain affects the body underscores the need to address it proactively. While occasional stress is unavoidable, prolonged tension requires appropriate interventions to maintain overall well-being. Practicing mindfulness, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining healthy sleep patterns are some ways individuals can manage strain effectively.