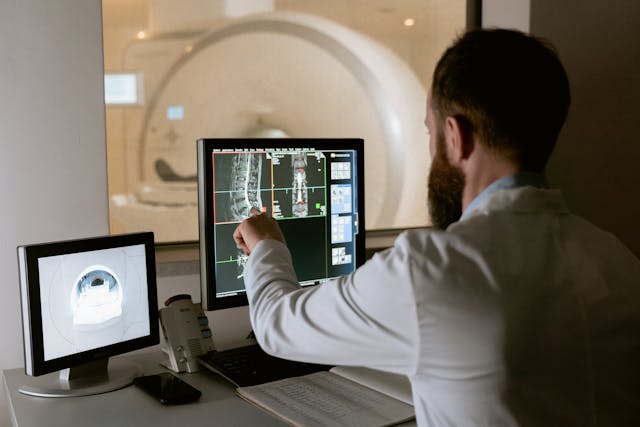
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan, or CAT scan, is a medical imaging technique that uses specialized X-rays to produce detailed, cross-sectional images of the body. Unlike regular X-rays, primarily used to view bones, these scans provide comprehensive images of bones, organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues. CT scans are invaluable tools for diagnosing various health conditions. They also help guide treatment plans and monitor patients’ progress during medical care.
Differences Between CT Scans and Other Imaging Tests
CT scan technology stands out for its ability to create highly detailed 3D images. While traditional X-rays effectively detect fractures and other bone-related issues, this method combines multiple X-ray images from different angles to provide clear, cross-sectional views of internal structures. CT imaging offers faster results than MRI scans, which rely on magnetic fields. MRI scans are particularly effective for soft tissues like muscles or ligaments and are often the preferred choice in emergencies.
The Process of Undergoing a CT Scan
Undergoing a CT scan is a streamlined and non-invasive process. Patients lie on a motorized table that moves through the circular opening of the CT machine. The machine emits a narrow X-ray beam that rotates around the body, capturing multiple images or “slices.” A computer then reconstructs these slices into detailed 2D or 3D images. For specific CT imaging, a contrast dye may enhance the visibility of specific structures, such as blood vessels or gastrointestinal organs. Depending on the particular diagnostic need, this dye can be introduced orally, intravenously, or through an enema.
Conditions Diagnosed by CT Technology
CT imaging has proven instrumental in diagnosing numerous previously undetected health conditions. These include but are not limited to:
- Internal injuries, such as fractures or organ damage.
- Head injuries, including swelling or bleeding in the brain.
- Lung diseases, like pneumonia or interstitial lung disease.
- Gastrointestinal disorders, including intestinal blockages or tumors.
- Conditions involving blood vessels, such as clogged arteries and aneurysms.
- Various cancers, including brain, colon, or lung cancer.
Benefits of Early Detection With CT Scans
One of the most significant benefits of CT imaging is the early detection of health conditions. By identifying abnormalities early, CT technology empowers healthcare providers to initiate timely interventions. This can lead to more effective treatment plans, better patient outcomes, and a reduced likelihood of complications. The detailed images provided by CT technology also allow medical practitioners to diagnose problems that may not be evident through physical examination or basic diagnostic tests.
Risks and Limitations of CT Imaging
CT imaging is generally safe but does involve low levels of radiation exposure. The risks are minimal compared to its diagnostic benefits, especially in urgent cases. In rare instances, contrast dyes used during the procedure can cause mild allergic reactions. CT technology may not fully detect conditions like soft tissue injuries or non-calcified abnormalities. For these cases, an MRI is often more effective. Pregnant individuals are usually advised to avoid CT imaging to minimize potential risks to the fetus.
Also Read: GPs to Offer Ultrasound for Suspected Endometriosis
Embracing Advanced Diagnostic Tools
CT technology is integral to modern diagnostic imaging, helping identify undiagnosed health conditions across various body areas. Its ability to produce detailed images and contribute to personalized medicine transforms healthcare. Contact a diagnostic imaging center near you if you believe you or a loved one could benefit from a CT scan.